Renewable Gas
Renewable Gas is a term used to describe gases that can be used as a clean energy source which do not produce any additional emissions when you burn them. This makes renewable gas a more sustainable option for the environment compared to natural gas and one viable energy pathway for Australia to reduce its emissions as we head towards a low carbon, sustainable future.
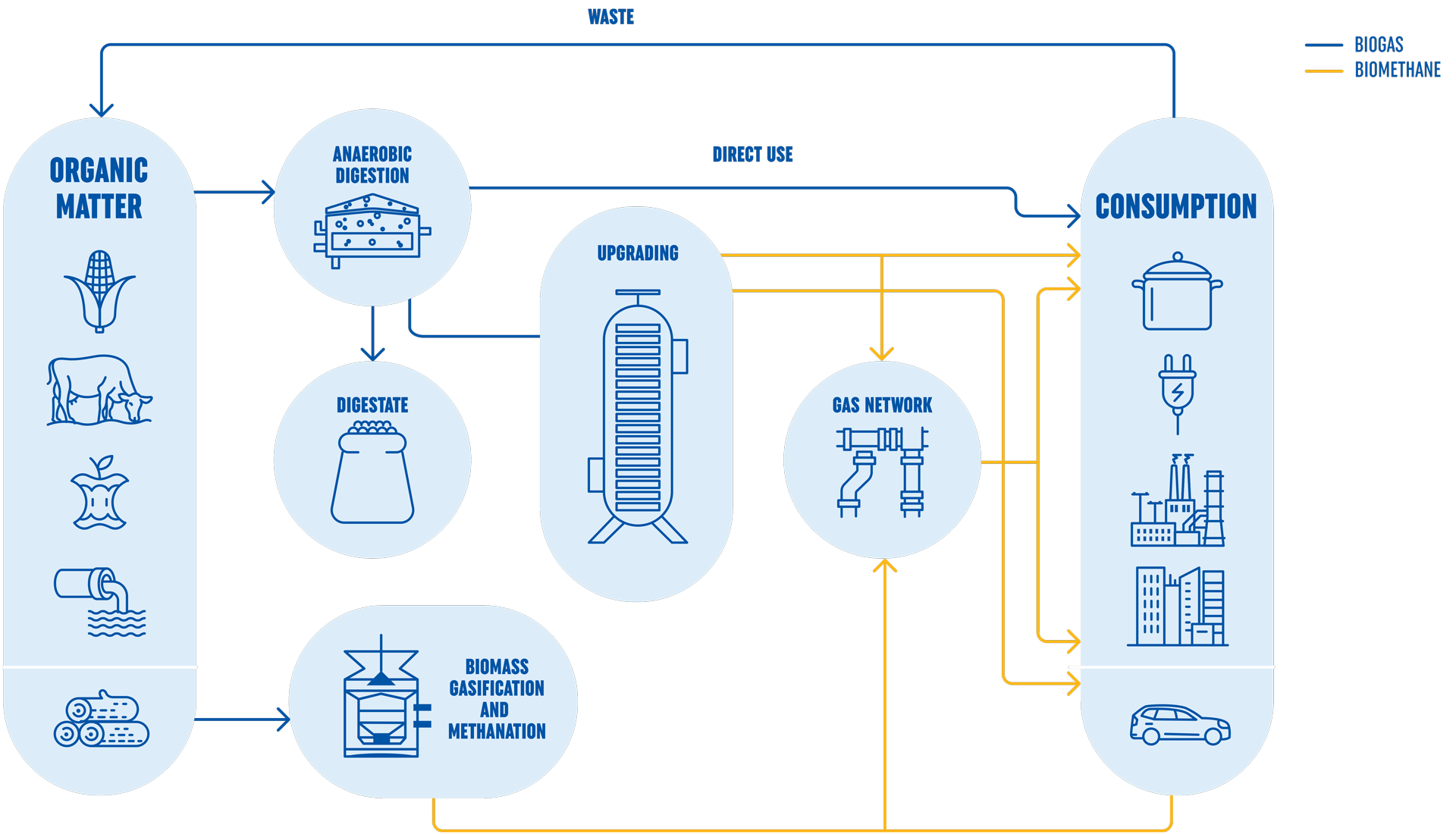
Renewable hydrogen and biomethane are the most common forms of renewable gas. Biomethane is made from biogas, which can be sourced from various forms of organic material such as green waste, food, industry by-products, agricultural residues, and industrial waste. Biomethane is a renewable gas that can replace natural gas without any modifications to existing gas networks or appliances.
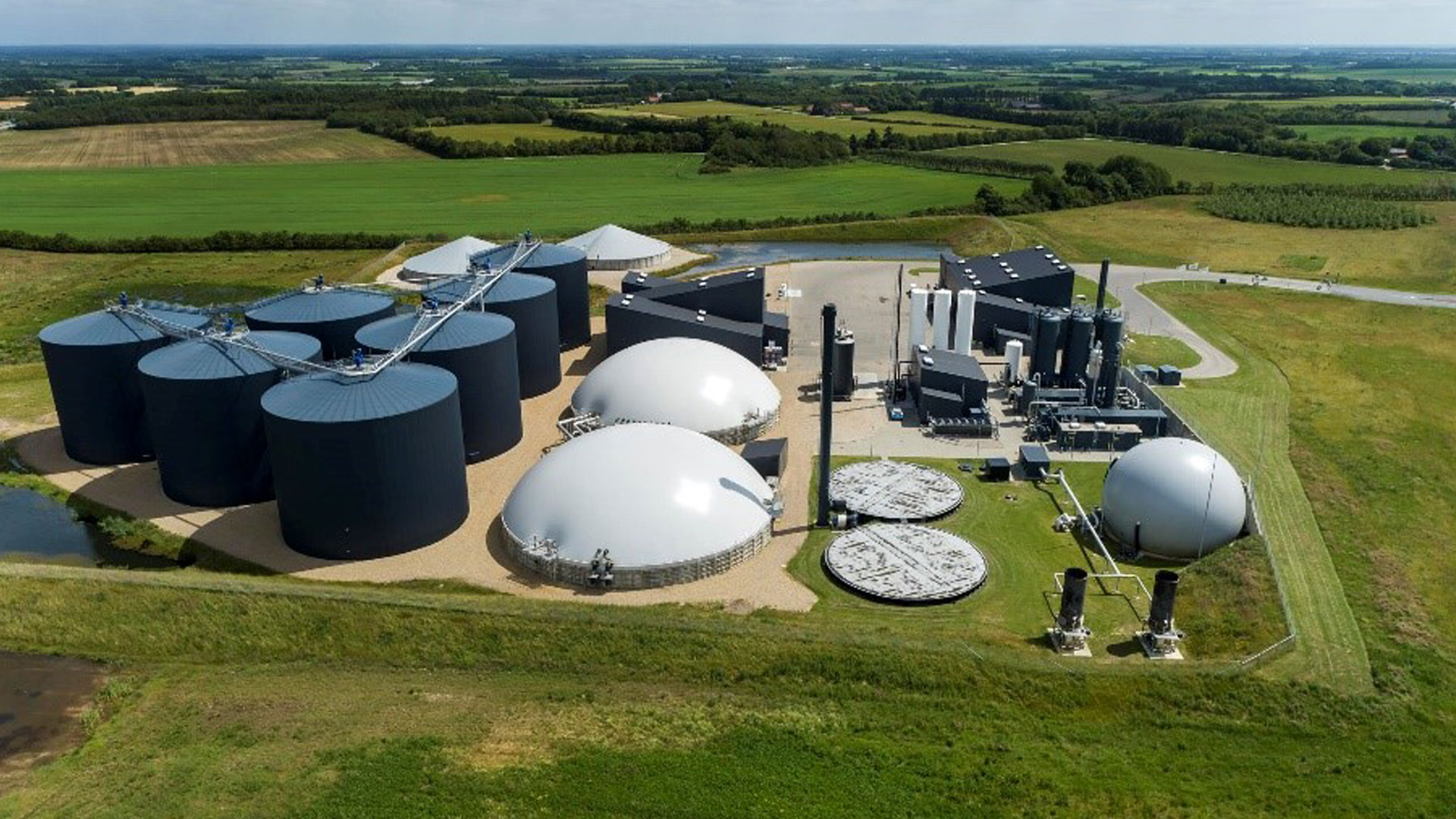
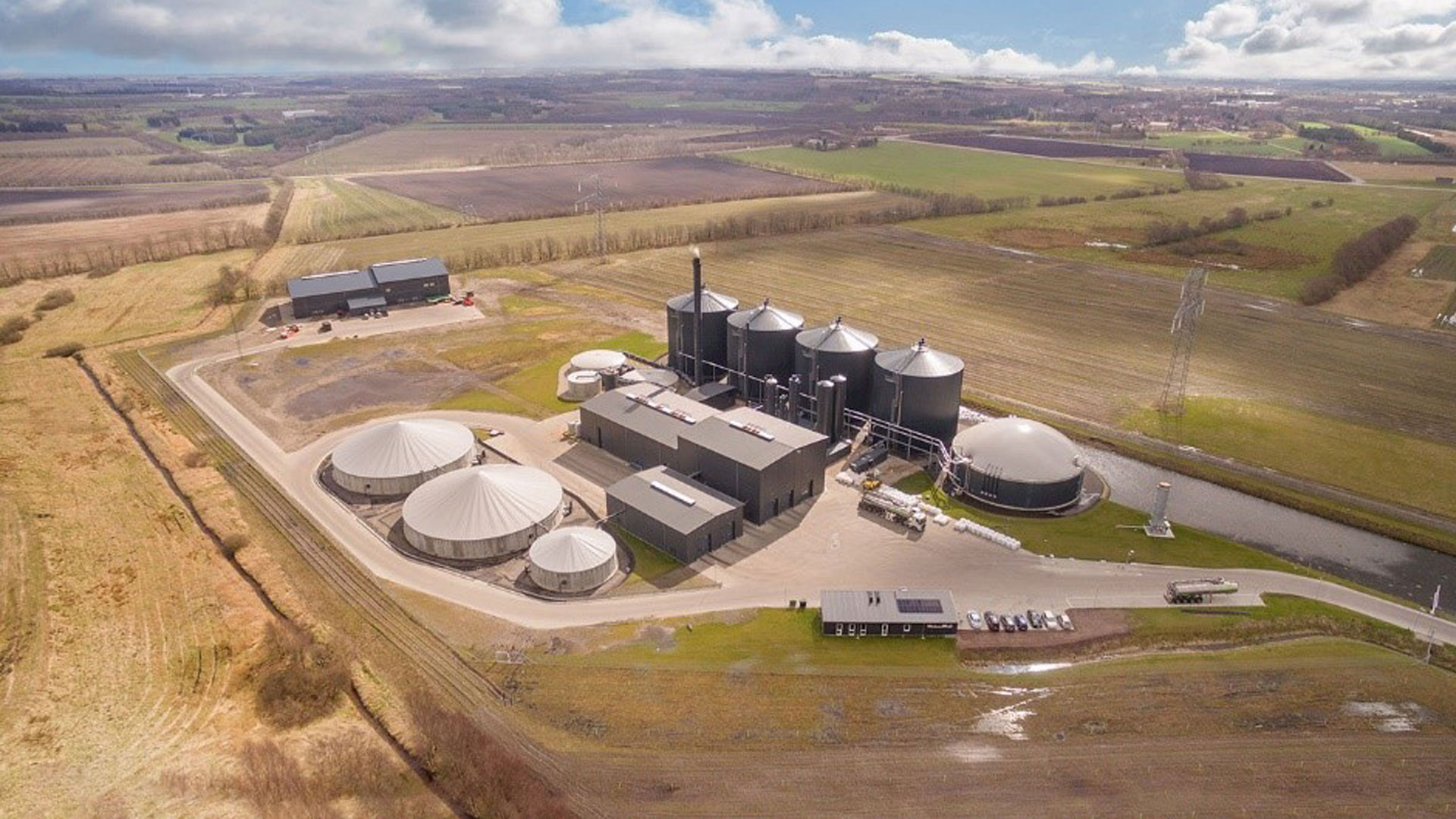
Biogas is produced through a process known as anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down raw materials such as agricultural waste, sewage, landfill, and plant material in an oxygen-free environment. The biogas released in the process is predominantly methane (60%), with the remaining 40% consisting of carbon dioxide and trace elements such as hydrogen sulphide, nitrogen, and oxygen. By removing the CO2 and other elements, the biogas can be upgraded to biomethane, resulting in an almost pure methane product.
In the current energy market, biogas is primarily used to generate electricity or is burnt off. However, we have an exciting opportunity to upgrade biogas to biomethane and supply it to households and businesses.
The Process
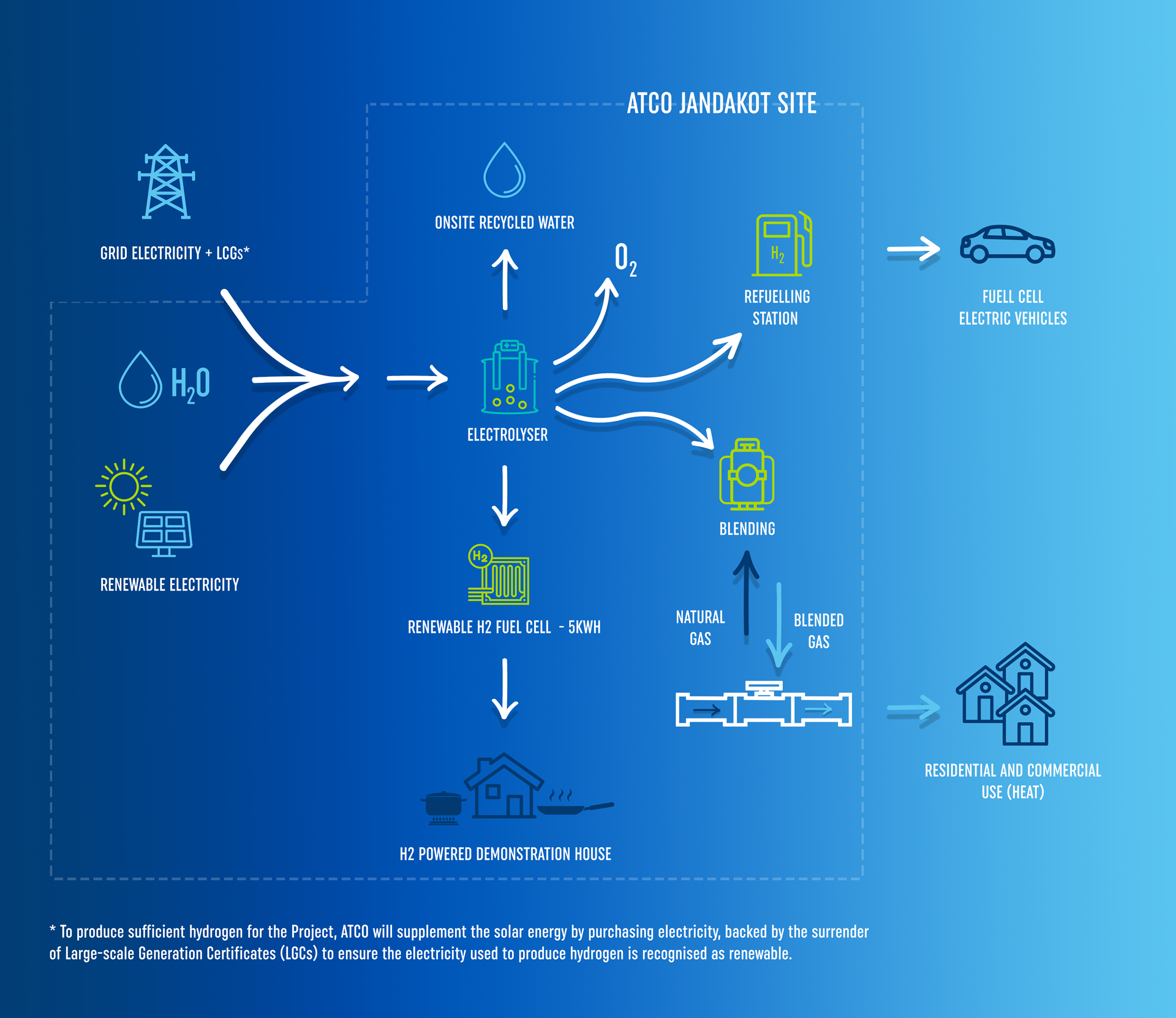
Another example of a renewable gas is Renewable Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe and can be produced using various methods, the most environmentally friendly way being electrolysis, using renewable electricity. This process involves passing an electrical current through water and separating it into hydrogen and oxygen.
When burnt, hydrogen primarily releases heat and water vapour, which is non-toxic. Hydrogen could be blended with natural gas or biomethane and delivered to homes and businesses through existing gas networks or stored for later use.
In the home, like natural gas, hydrogen can be used for heating, hot water, and cooking. It has many more uses in industry such as in steel making, ammonia production, rocket fuel, semiconductor manufacturing, welding, and methanol production.
With the help of State and Federal governments, as well as industry, Australia is shaping up to be a big global player in the renewable hydrogen market. ATCO is currently trialling hydrogen blending into the existing gas network with volumes of up to ten per cent, and is advising industry and government on large-scale renewable hydrogen production.
There are several large global Renewable Gas projects that are being developed or have already been implemented:
The process of producing Renewable Gas from organic waste can help to reduce methane emissions from the decomposition of waste in landfills.
- Supporting circular economy: Renewable Gas is often produced from organic waste materials such as agricultural waste, food waste, and wastewater. By using these waste materials to produce energy, a circular economy can be created, where waste is transformed into a valuable resource.
- Improving air quality: When used as a transportation fuel, Renewable Gas can significantly reduce emissions of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can have negative impacts on human health and the environment.
- Creating local jobs: The production of Renewable Gas can create local jobs in the agriculture, waste management, and energy sectors, supporting local economies.
Overall, Renewable Gas can provide a renewable source of energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, support a circular economy, and improve air quality.





